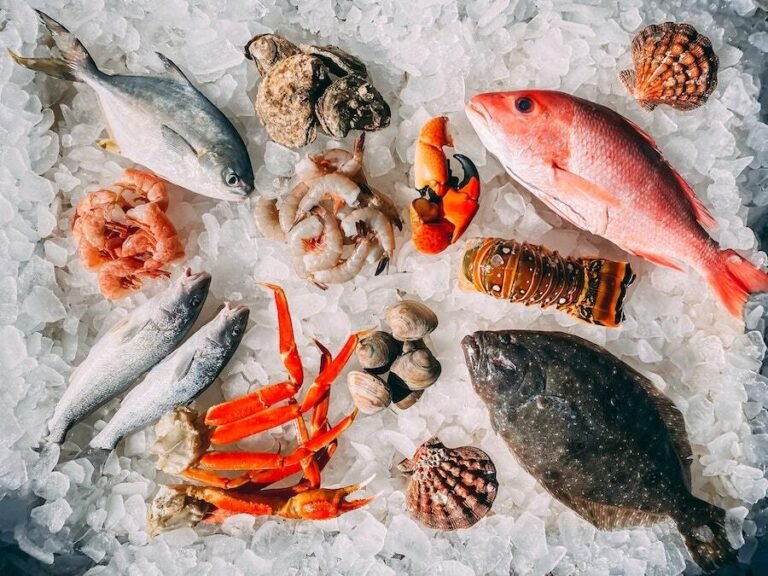
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that offer numerous health benefits, from improving heart health to supporting brain function. While many fish species contain omega-3s, some stand out as particularly rich sources. Let’s dive into the world of omega-3 rich fish and explore the top contenders.
Cold-Water Fatty Fish
Cold-water fatty fish are renowned for their high omega-3 content. These fish live in colder waters, which forces their bodies to produce more omega-3s to stay warm. Some of the most notable examples include:
- Salmon: Salmon is perhaps the most well-known source of omega-3s. It’s packed with both eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), two essential types of omega-3s.
- Mackerel: This small, oily fish is a nutritional powerhouse, offering a high concentration of omega-3s along with other essential nutrients.
- Sardines: Sardines are another excellent source of omega-3s, and they’re also rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein.
- Herring: This small, silvery fish is a great option for those seeking a high omega-3 content.
- Anchovies: Anchovies are often overlooked, but they are packed with omega-3s and other essential nutrients.
Lesser-known Omega-3 producers
While cold-water fatty fish are the most well-known sources of omega-3s, there are other fish species that also offer significant amounts:
- Tuna: While tuna can vary in omega-3 content depending on the species and size, it is still a good source of these essential fatty acids.
- Trout: Trout, especially wild-caught trout, is a nutritious fish that contains a good amount of omega-3s.
- Halibut: Halibut is a larger fish that is also a decent source of omega-3s.
- Cod: While cod is lower in fat than some other fish, it still offers a moderate amount of omega-3s.
Factors affecting Omega-3 content in fish
The omega-3 content of fish can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Fish species: Different fish species have varying levels of omega-3s.
- Fish size: Larger fish tend to have higher levels of omega-3s than smaller fish.
- Fish diet: The type of food a fish eats can affect its omega-3 content. Fish that consume plankton and other small organisms tend to have higher levels of omega-3s.
- Fishing location: The location where the fish is caught can also influence its omega-3 content. Fish from colder waters generally have higher levels of omega-3s than fish from warmer waters.
Incorporating Omega-3-Rich Fish into Your Diet
To maximize the benefits of omega-3s, aim to eat two to three servings of fatty fish per week.
- How to Incorporate Fatty Fish into Your Diet
There are many delicious ways to enjoy fatty fish.
Here are some ideas:
- Grilled or Baked: Grilling or baking fish is a healthy and flavorful way to prepare it.
- Poached: Poaching fish in a light broth or lemon juice can help retain its delicate flavor.
- Salads: Add flaked salmon, mackerel, or sardines to your favorite salads for a boost of protein and omega-3s.
- Sushi: Sushi is a popular way to enjoy fish, and it offers a variety of options, from classic rolls to nigiri.
- Fish Tacos or Burritos: Create a healthy and delicious meal by incorporating fish into tacos or burritos.
- Fish Chowder or Soup: Warm up with a hearty fish chowder or soup.
Remember: While fish is an excellent source of omega-3s, it’s important to be mindful of mercury levels. Some fish, such as shark, swordfish, and tilefish, can be high in mercury. It’s best to limit your consumption of these fish or avoid them altogether.
By incorporating omega-3-rich fish into your diet, you can reap the numerous health benefits associated with these essential fatty acids. Whether you’re looking to improve heart health, brain function, or overall well-being, omega-3s are a valuable addition to your diet.