Fungal infections are highly prevalent, catching even the healthiest individuals off guard at times.
The body’s defense mechanism against such sneaky fungi works throughout but on occasions, they get a chance when we are weak. Being unwell, stressed, or just about anything else can make one vulnerable to these infections and during such times knowing how our immune systems respond becomes important for staying healthy.
You can keep these troublesome intruders at bay by understanding the risk factors associated with fungal infections and learning ways to boost your natural immunity.
What Is Fungal Infection?
A fungal infection occurs when harmful fungi enter the body and grow, typically affecting the skin, nails, lungs, or other areas.
The severity of these infections can vary from a mild case such as athlete’s foot to more serious cases that need medication, especially among immunocompromised individuals.
| Note: Fungal illnesses result in about 75,000 hospital admissions and around 9 million outpatient visits every year annually. |
What Does Fungal Infection Look Like?
Fungal infections most often manifest as red, itchy rashes, scaly patches, or blisters of the skin. They also may manifest as discolored nails, a thickening of the nail, or brittleness. Sometimes, they create white patches in the mouth or throat. They could cause respiratory symptoms if the lungs become infected.
A fungal infection can be treated and gotten rid of by the use of over-the-counter medications like antifungal lotions, powders, and sprays. The fungus eliminator is made to precisely target the afflicted region. Your doctor can also recommend oral antifungal medication for an infection that is serious or for a more serious nail issue.
You can also avoid the spread of infection by keeping the area clean and dry, avoiding sharing personal items, and practicing good hygiene.
Symptoms of Fungal Infection
Symptoms of fungal infections can include,
- The skin is generally itchy: Red, itchy patches that may be flaky.
- Rashes: Scaly or discolored skin that can spread.
- Blisters: Small bumps filled with fluid that may ooze.
- Nail Changes: Thickened, discolored, or brittle nails.
- White Patches: White spots inside the mouth or throat.
- Respiratory Issues: Coughing or difficulty breathing if the lungs are infected.
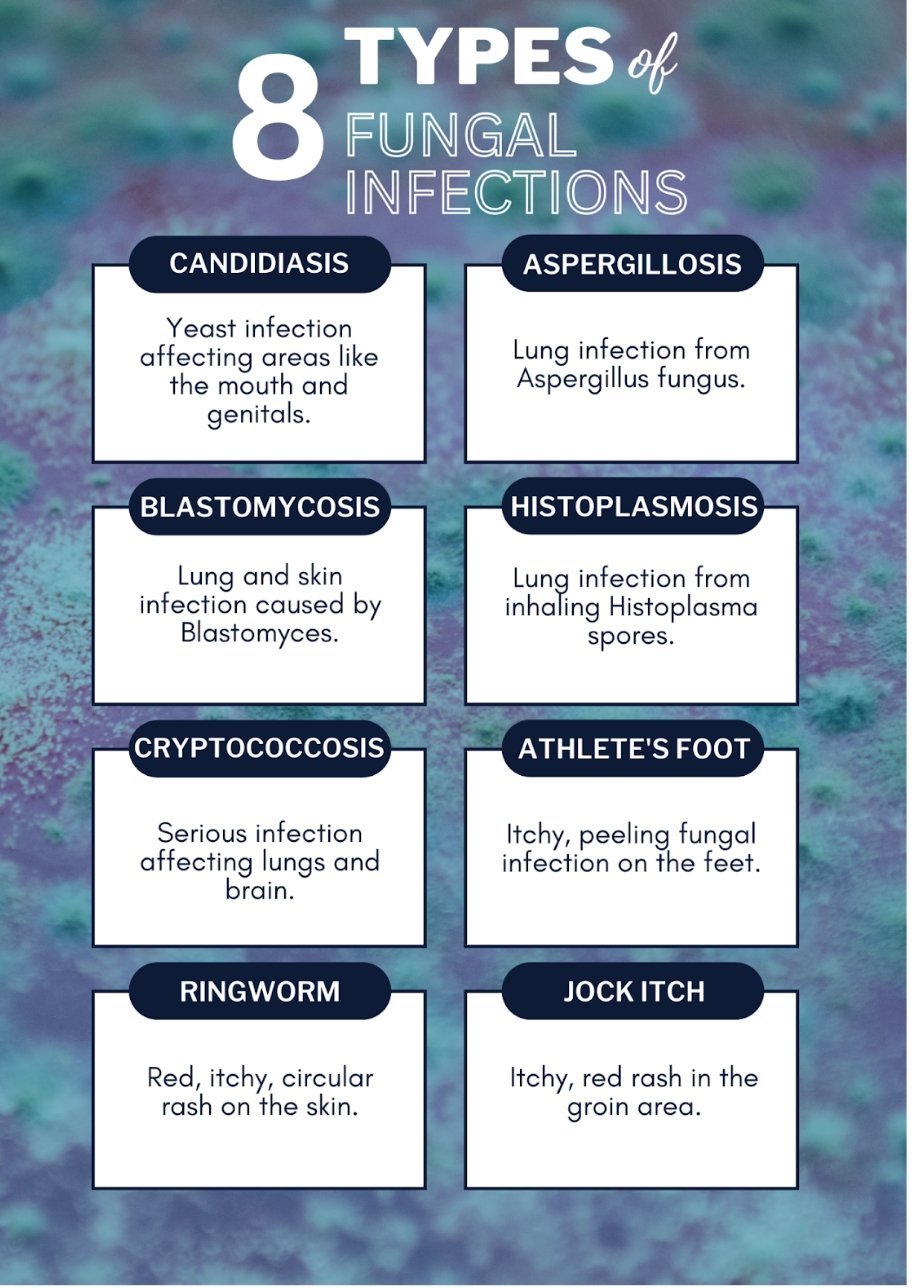
Types of Fungal Infections
How Fungi Interact With Our Immune System
Fungi are found everywhere, but only a few pose grave health problems. Examples include Candida, which causes infections like thrush and candidiasis. Aspergillus, which causes respiratory problems, especially in people with poor immune systems, and Cryptococcus, responsible for severe illnesses among those infected with HIV/AIDS.
Such infections can be countered by our body in two ways: one is through the action of innate immunity, which acts very rapidly and is broad with means of physical barriers and general immune cells. The other way adaptive immunity presents is a more targeted reaction with the involvement of T-cells and antibodies that specifically deal with the fungi.
Both macrophages and T lymphocytes are involved in the identification and elimination of fungi before they cause infection. However, fungi have developed some mechanisms useful for overcoming our immune defense.
They may undergo surface modification to evade the recognition of the immune system, secrete substances that impede our immunological response, or penetrate our cells, which complicates the curing of chronic infections.
Factors Weakening the Immune System and Increasing Fungal Infection Risk
Several factors can compromise our immune defenses, leaving us more susceptible to fungal infections:
- The immune system may get weakened due to certain diseases such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, organ transplants, or diabetes creating the danger of fungal infections.
- Additionally, antifungal drugs or even chemotherapy can lower our defenses against fungi and require monitoring (immune-reducing).
- Environmental conditions such as poor dietary habits, chronic stress, and exposure to fungal spores also increase the risk of infection.
The Role of Antifungal Treatments and Immune Modulation
As far as the treatment of a fungal infection is concerned, one has to focus on the eradication and killing of the particular fungi that create the problem by antifungal treatments.
Such medications may effectively address the infection, however, they usually possess certain weaknesses, such as side effects or medication interactions.
Researchers are working to improve these therapies by exploring new approaches, such as combining treatments and boosting the body’s immunity. Immunity against these organisms can also be raised by modifying diet. Hence, making the organisms less capable of infecting us successfully.
In this vein, the researchers suggested the following new strategies for the improvement of therapy: combination therapies, enhancement of immune support, and targeted drug delivery systems. Moreover, it can be of great help to the immune system if it is allowed to defeat the fungal infection naturally.
This might involve certain dietary supplements, including vitamins C and vitamin D, zinc, and probiotics; lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management; or even some emerging immunotherapies that are currently being explored.
Prevention and Early Detection of Fungal Infections
It is important to prevent and identify fungal infections early on, especially for those who are more susceptible.
The first step in this process is to track possible signs or symptoms of a possible infection that can cause harm. They should maintain cleanliness, avoid areas where fungi grow, use personal protective equipment as needed, and follow safe food handling practices.
Additionally, regular health check-ups are important for high-risk groups, which may require periodic blood tests routine as well as skin examinations together with computed tomography (CT) scans or chest X-rays among others if they are at risk of lung diseases.
These measures help in promoting early diagnosis and decreasing the chances of encountering serious fungus infections at any point in life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What drink kills fungus?
Due to their antifungal qualities, beverages like apple cider vinegar and grapefruit juice can help stop the growth of fungi. They have to be incorporated within a more comprehensive therapy strategy, though.
- What is the most common fungal infection?
Some common fungal infections are ringworm and vaginal yeast infections. Usually, ringworm causes a ring-like rash that easily spreads from person to person or from pets to humans. The fungi responsible for ringworm can also lead to jock itch, athlete’s foot and nail infections.
- What happens if you have a fungal infection for too long?
Prolonged fungal infection can affect other areas of the body and escalate other bodily ailments, thus making it more severe. Therefore, to avoid other complications, treatment must be started early.
Key Takeaways
Fungal infections represent a significant health challenge, particularly for those with compromised immune systems. There are several reasons things such as fungal infections pose a serious threat, especially for those whose immunity is weak.
In addition to that, fungal diseases remain a big problem as far as an individual with a weak immune system is concerned. To devise better preventative strategies, there is a need to understand how fungi interact with our immune systems.
For us to effectively manage and diminish the risk of fungal infections, it would be necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, look out for early symptoms, and then seek medical advice before it is too late. This will not only result in good health but also improve self-defense against such threats.

Daniel J. Morgan is the founder of Invidiata Magazine, a premier publication showcasing luxury living, arts, and culture. With a passion for excellence, Daniel has established the magazine as a beacon of sophistication and refinement, captivating discerning audiences worldwide.





