Key Takeaways
- Ultrasound is a non-invasive, radiation-free imaging technique for IBD monitoring.
- Regular monitoring helps in timely diagnosis and treatment adjustments.
- Comparative advantages over other imaging modalities.
- Importance of patient comfort and accessibility in IBD management.
Introduction to Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) encompasses conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. These conditions can lead to a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and even serious complications if left unmanaged. Accurate monitoring plays a crucial role in managing these conditions effectively. Among the various monitoring tools available, intestinal ultrasound stands out for its safety, effectiveness, and convenience. This technology aids in visualizing the state of the intestines, providing vital insights that can guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.
The Role of Ultrasound in IBD Monitoring
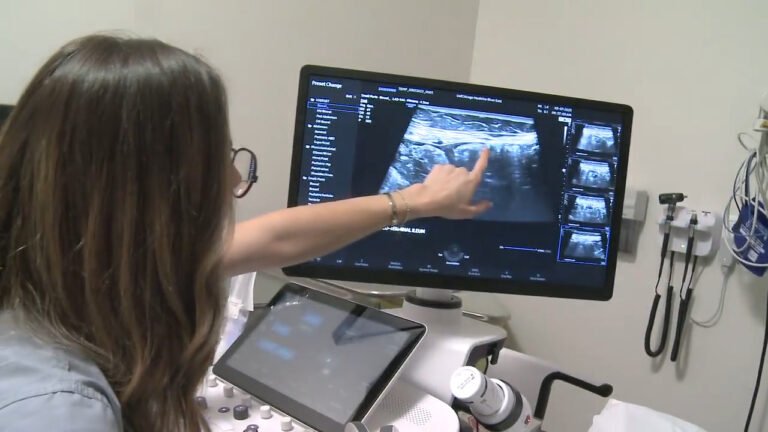
Ultrasound, especially intestinal ultrasound IUS, has become a key tool in monitoring IBD. Unlike traditional imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans, ultrasound offers a non-invasive and radiation-free alternative, making it an attractive option for regular use. The technique utilizes high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the intestines, allowing healthcare providers to assess the level of inflammation, detect complications, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments in real-time. Furthermore, the ability to employ ultrasound at the bedside means that results can be obtained swiftly, potentially leading to immediate adjustments in clinical management.
Benefits of Ultrasound in IBD Management
One of the primary advantages of using ultrasound in IBD management is its capability to provide real-time imaging. This facilitates an immediate assessment of disease activity, allowing physicians to make timely and well-informed adjustments to treatment plans. This cannot be overstated, as timely intervention can significantly impact patient outcomes. Moreover, the absence of radiation in ultrasound imaging makes it considerably safer for repeated use, which is often necessary in chronic conditions like IBD. Patients can undergo multiple scans throughout treatment without the cumulative risks associated with radiation exposure, contributing to safer overall healthcare management.
Comparative Advantages Over Other Imaging Techniques
Ultrasound stands out when compared to traditional methods such as CT scans and MRI. While those techniques provide detailed images, they often involve exposure to radiation or the need for contrast agents. These elements can pose risks, especially with frequent use. Conversely, ultrasound is safe, radiation-free, and highly effective in identifying active disease segments and complications, such as abscesses or strictures. This advantage is particularly notable given the chronic nature of IBD and the need for frequent monitoring. For instance, while CT scans expose patients to substantial levels of radiation, ultrasound provides equal, if not superior, diagnostic capabilities without these risks.
Patient Comfort and Accessibility
Another significant advantage of ultrasound is the comfort it offers to patients. The procedure is quick, painless, and requires no special preparation, making it a more patient-friendly option. This ease and comfort enhance patient compliance, as individuals are more likely to agree to regular monitoring when the procedure does not cause discomfort or require extensive preparation. Accessibility is also a major factor—ultrasound machines are widely available in most clinical settings, including outpatient clinics and community health centers. This increased accessibility ensures that patients receive timely scans without needing specialized appointments or travel, facilitating ongoing management and early detection of relapses.
Supporting Data and Research
Recent studies have highlighted the efficacy of ultrasound in detecting inflammation and assessing IBD activity. For instance, a Medical News Today article discusses how advancements in ultrasound technology contribute to better diagnosis and management of IBD. These studies demonstrate that ultrasound can achieve comparable accuracy to MRI detecting bowel inflammation and other IBD-related complications. Furthermore, the real-time imaging capabilities of ultrasound facilitate more accurate and quicker assessments compared to other modalities, underscoring its role as a first-line imaging choice in many clinical scenarios.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ultrasound is revolutionizing how we monitor and manage Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Its non-invasive nature, safety profile, and real-time imaging capabilities make it an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals. Additionally, ultrasound’s ability to provide immediate and important diagnostic information without the risks associated with radiation exposure marks a significant advancement in medical imaging for chronic conditions. As research continues to support its benefits and more clinicians become proficient with its use, we can expect increased adoption of ultrasound in IBD management protocols, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Passionate content writer and savvy blog publisher, Aamir crafts compelling stories and insightful articles that captivate and inform. With a knack for blending creativity and strategy, they bring fresh perspectives to every piece. Dive into their world of words and discover content that resonates.